Many women notice various changes in their bodies, some of which might seem insignificant. However, unexpected facial hair, particularly those annoying chin whiskers, could indicate an underlying condition known as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Let’s delve into what PCOS is, its causes, symptoms, and why it’s essential to address changes in facial hair or other related symptoms promptly.
Understanding PCOS: More Than Just Hormonal Imbalance
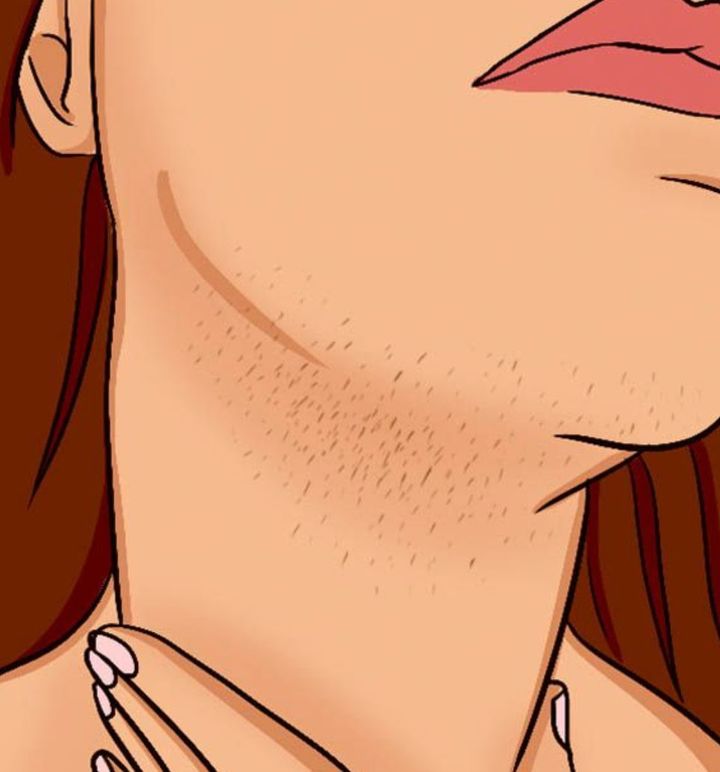
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects many women, yet a significant number are unaware they have it. Primarily a hormonal disorder, PCOS causes symptoms like irregular periods, facial hair (particularly on the chin, upper lip, or sideburns), acne, and weight gain.
“Polycystic” refers to the numerous small cysts that can form on the ovaries. While these cysts are harmless, they cause a hormonal imbalance that disrupts normal bodily functions. This imbalance can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and even unusual hair growth in areas most women don’t typically experience it, such as the chin or chest.
The Hidden Risks of PCOS: More Than Just Facial Hair
While symptoms like facial hair or acne might seem like mere inconveniences, untreated PCOS can lead to serious long-term health issues. Women with PCOS have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic disorders.
Early diagnosis is essential to prevent these complications. Managing PCOS isn’t just about addressing visible symptoms like facial hair; it’s about maintaining overall health to prevent future complications.
What Causes PCOS? Exploring The Theories
The exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, but several factors may increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Here are some widely accepted risk factors:
1. Excess Insulin
One theory is that excess insulin plays a significant role in PCOS development. Insulin helps your body use sugar from carbohydrates for energy. Overproduction of insulin can lead to increased androgen production (male hormones) in the ovaries, interfering with regular ovulation and causing symptoms like irregular periods and facial hair growth.
2. Low-Grade Inflammation
Research indicates that women with PCOS often experience low-grade inflammation, which can stimulate polycystic ovaries to produce excess androgens. This increase in male hormones contributes to many PCOS symptoms, including facial hair and acne.
3. Heredity
PCOS can run in families. Women whose mothers or sisters have PCOS are more likely to develop it. While genetics don’t guarantee PCOS, they significantly increase the risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms of PCOS
PCOS symptoms can start shortly after menstruation begins but may also develop later due to weight gain or other factors. Not every woman will have the same symptoms, and severity can vary, especially if obesity is a factor. Here are common symptoms to watch for:
1. Irregular Periods

Women with PCOS often have irregular menstrual cycles, such as cycles longer than 35 days, fewer than eight periods a year, prolonged periods, or complete absence of menstruation for several months. Unpredictable or unusually heavy periods could indicate PCOS.
2. Excess Facial and Body Hair (Hirsutism)
One of the most noticeable signs of PCOS is facial hair growth in patterns typical of male hair growth, such as the chin, upper lip, chest, stomach, and toes. This condition, known as hirsutism, is due to increased production of male hormones (androgens).
3. Mood Swings and Depression

PCOS can also affect emotional well-being. Women with PCOS are more prone to mood swings, depression, and anxiety. Managing these emotional symptoms can be as challenging as dealing with the physical ones.
4. Acne and Oily Skin
Another sign of PCOS is deep, painful, and persistent acne. Excess androgens in women with PCOS stimulate oil production, leading to very oily skin and acne that may not respond to typical over-the-counter treatments.
5. Insulin Resistance
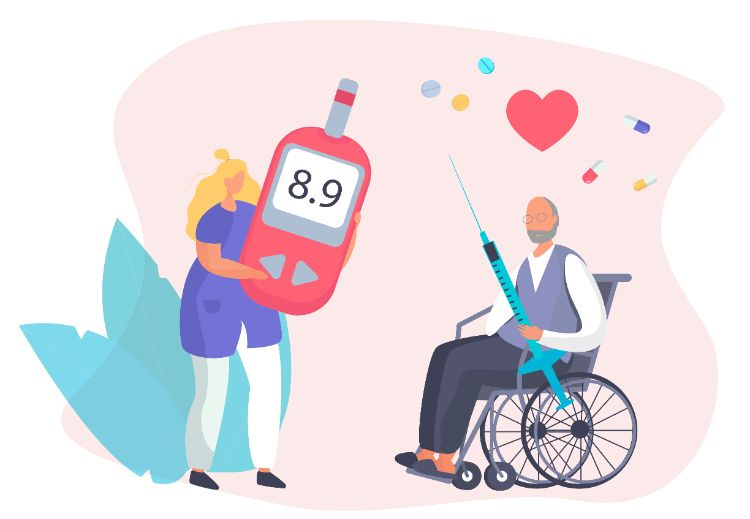

Insulin resistance is common in women with PCOS, making it harder for the body to use insulin effectively. This can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes over time.
Treatment Options: Managing PCOS Effectively
PCOS is a lifelong condition, but you can manage it with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. Your doctor may suggest various treatments based on your symptoms and health needs:
1. Lifestyle Changes
For many, lifestyle changes are the first treatment step. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce PCOS symptoms. Even a small weight loss, as little as 5%, can significantly manage the condition.
2. Medications

Doctors may also prescribe medications to regulate hormones. Birth control pills can regulate periods, lower androgen levels, and reduce symptoms like excess hair growth and acne. For women wanting to conceive, medications might be prescribed to stimulate ovulation.
3. Insulin Sensitizers
If insulin resistance is an issue, medications like metformin can enhance your body’s insulin sensitivity, aiding in weight management and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion: Don’t Ignore the Signs of PCOS
If you notice changes in your facial hair or any other symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to consult your doctor. While chin whiskers might seem like a minor issue, they could be an important indicator of PCOS—a condition that requires early diagnosis and ongoing management. By taking action and seeking medical advice, you can manage symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications. So, if you’re experiencing these symptoms, don’t wait—your health is worth it!