Imagine being a carefree 10-year-old, enjoying a rural adventure in Brazil, only to return with a painful and alarming infestation of sand fleas. This was the unfortunate reality for one young girl, whose feet became severely infested with Tunga penetrans, commonly known as sand fleas, after she played barefoot in a pigsty. A disturbing image has now been released by the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), highlighting the extent of the infestation and the impact of tungiasis, an inflammatory skin disease caused by the female sand flea.
This case is a stark reminder of how seemingly innocent actions, like playing barefoot in rural areas, can lead to serious health complications. In this article, we’ll explore what tungiasis is, how it spreads, and the steps taken to treat the girl’s painful condition.
What Is Tungiasis? Understanding the Sand Flea Infestation
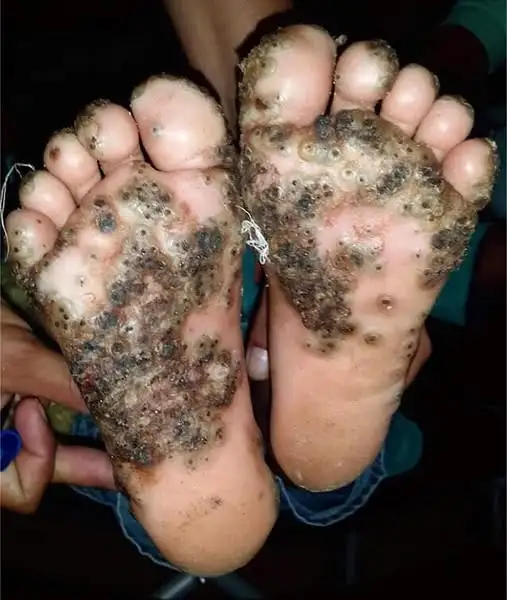
Tungiasis is a parasitic skin disease caused by the female sand flea, Tunga penetrans. Found primarily in tropical and subtropical regions, the sand flea burrows into the skin, particularly around the feet, where it causes intense itching, pain, and inflammation. The disease is most commonly associated with sandy areas like beaches, farms, and animal stables.
The female sand flea’s life cycle begins when it burrows into the skin, where it grows rapidly, increasing its body volume by up to 2,000 times. The flea’s presence leads to severe irritation and local swelling. Infected individuals often experience painful lesions with a dark central dot—typically where the flea is located. As the flea grows, it can cause bacterial infections, abscesses, and even impair mobility due to the pain and swelling.
The Disturbing Case of a 10-Year-Old Girl in Brazil
During a recent trip to rural Brazil, a 10-year-old girl’s carefree barefoot play in a pigsty led to her being infested with sand fleas. After experiencing persistent itching and painful lesions on the soles of her feet for 10 days, her family sought medical attention. Upon examination, the doctors found black dots in the center of the lesions, a telltale sign of tungiasis.
A family history revealed that the girl had been playing in the pigsty without shoes, exposing her feet to the sand fleas that were present in the area. After a thorough examination, sand fleas were removed from the affected areas, and tungiasis was officially diagnosed.
Symptoms of Tungiasis: What to Look For
Tungiasis can present itself in several ways, and its symptoms are often easy to misidentify as general skin irritations. The most common symptoms include:
- Itchy skin lesions: As the flea burrows into the skin, it causes intense itching and irritation.
- Painful, inflamed spots: The affected area swells, and lesions may become painful.
- Dark spots: These are often visible in the center of the lesions, indicating the presence of the flea.
- Bacterial infections: If left untreated, the lesions can become infected, leading to abscesses or even more severe complications like lymphangitis.
In the case of the young girl, she had been suffering from these symptoms for several days before being seen by medical professionals. Thankfully, after the fleas were removed and the lesions treated, her condition improved, and she experienced full recovery without any long-term complications.
How Do Sand Fleas Spread and How to Avoid Them?
Tunga penetrans, the sand flea responsible for tungiasis, thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. The fleas are typically found in sandy, rural areas, such as pigsties, farms, beaches, and stables. They are highly attracted to animals, particularly those with hoofs, which often carry the fleas on their bodies.

The fleas spread when they burrow into the skin of humans or animals in the area. While humans are the primary hosts, animals can also harbor the fleas, making them a vector for transmission. For those living in or visiting affected areas, here are some key prevention tips:
- Wear protective footwear: Always wear shoes, particularly in sandy areas or places known to harbor fleas.
- Avoid barefoot play in high-risk areas: Areas like pigsties, animal pens, and sandy beaches should be avoided for barefoot activities.
- Check feet regularly: If you’ve been in areas where sand fleas are common, check your feet for any signs of infestation.
Treatment for Tungiasis: How to Address the Infestation
Treating tungiasis typically involves removing the sand fleas from the affected skin and providing local wound care to prevent infection. In the case of the young girl, her medical team removed the fleas from multiple lesions and treated the wounds to avoid further complications.
Treatment steps include:
- Flea removal: A healthcare provider carefully removes the sand fleas from the skin, which often requires local anesthesia due to the pain and sensitivity of the affected areas.
- Local wound care: After flea removal, the wounds are cleaned and dressed to prevent secondary infections. Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacterial infections are present.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Follow-up care: Regular check-ups ensure that the infection doesn’t return and that healing progresses smoothly.
In most cases, once the fleas are removed, the symptoms begin to subside, and full recovery can occur with proper treatment. The girl in the case report fully recovered without any long-term issues.
Global Health Impact of Tungiasis

Tungiasis is not just a rare, isolated condition. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 20 million people in the Americas are at risk of tungiasis, especially in rural areas where sand fleas are common. The disease is particularly dangerous for vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly, as repeated infections can lead to long-term complications, including disfigurement and impaired mobility.
In rare cases, tungiasis can affect other parts of the body. For example, in 2018, a case from Nepal reported a man who had sand fleas burrowing into his genitals, a less common but serious manifestation of the disease. The man received treatment and recovered, but such cases highlight the potential for tungiasis to affect various body parts, leading to more severe health issues.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness and Prevention
The story of this young girl’s ordeal serves as a stark reminder of the risks posed by sand fleas in tropical and subtropical regions. While the condition is treatable, prevention is key to avoiding the painful and potentially serious complications of tungiasis. Wearing protective footwear and avoiding exposure to high-risk areas are simple steps that can go a long way in safeguarding your health.
As the case report demonstrated, early diagnosis and proper medical treatment are essential for a full recovery. It’s important to remain vigilant, especially when traveling to areas where sand fleas are prevalent, and take necessary precautions to protect yourself from this painful infestation.