n recent years, the rumor of plastic rice infiltrating the food supply has caused widespread concern among consumers. While the prevalence of this issue may be debated, the potential health risks of consuming adulterated grains are undeniable. As a proactive measure, it’s crucial to understand what plastic rice is, how to identify it, and why ensuring the authenticity of your food is so important.
Plastic rice is a term used to describe a purported counterfeit product that imitates the appearance of genuine rice. These synthetic grains are allegedly manufactured using a combination of synthetic materials, designed to mimic the look and feel of real rice. The primary motivation behind this deception is often financial, as the production of plastic rice may be a way for unscrupulous manufacturers to bypass food safety regulations and increase their profit margins.
Fortunately, there are several straightforward tests you can perform at home to determine if your rice is real or potentially adulterated. Let’s explore these methods in detail:
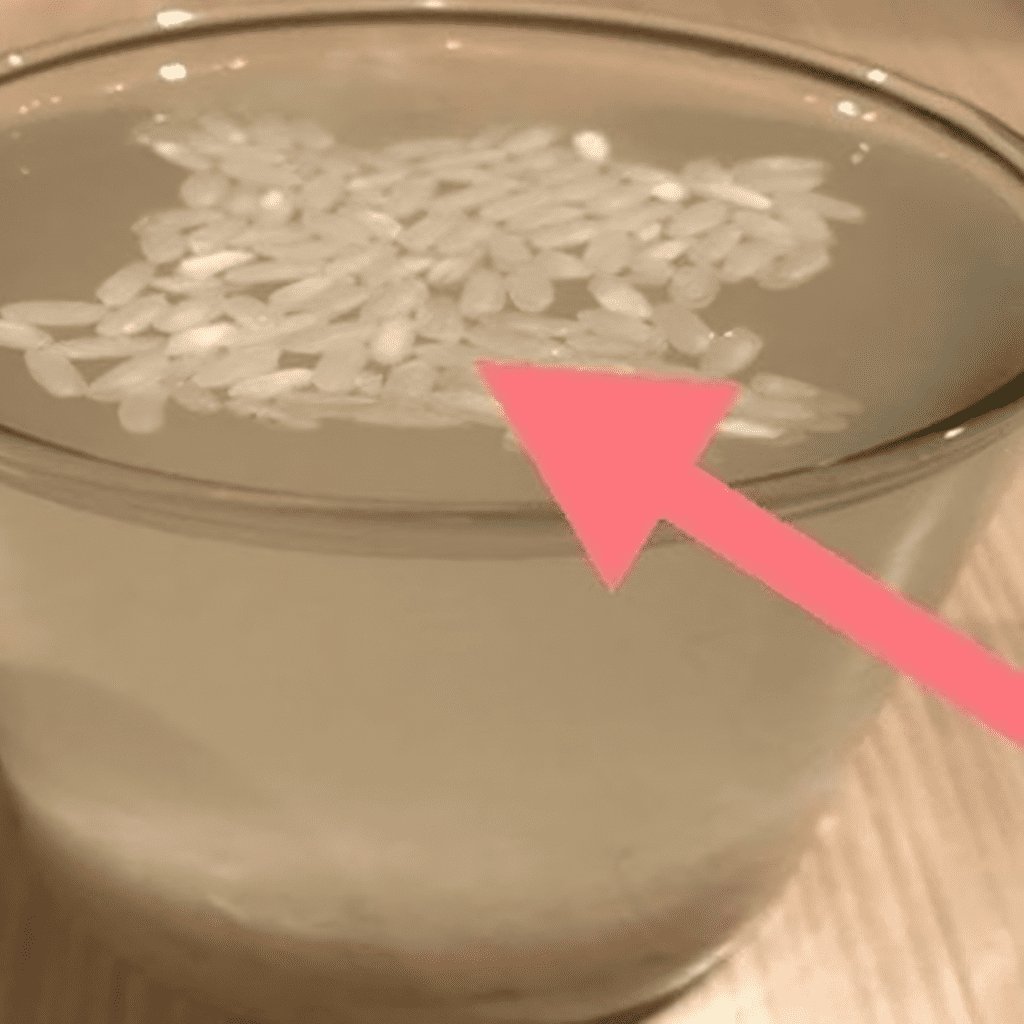

- The Water Test: Drop a tablespoon of rice into a glass of water and stir it. Genuine rice grains will sink to the bottom, while plastic grains are likely to float due to their lower density.
- The Fire Test: Hold a few grains of rice over a flame using a pair of tongs. Real rice will char and burn, releasing a toasted aroma. In contrast, plastic rice will melt and may emit a distinct plastic smell.
- The Mortar and Pestle Test: Crush a small sample of rice using a mortar and pestle. Genuine rice should powder easily and feel gritty, while plastic grains will not break down as readily and may have a more elastic texture.
- The Boil Test: Cook a small portion of the rice and observe the water. If you notice a significant amount of unusual residue, it could be a sign of impurities or additives. Real rice will have some starch that floats to the top, but it shouldn’t leave behind a substantial residue.
- The Mold Test: Cook a batch of rice and let it sit in a warm place for two or three days. If it’s authentic rice, it will begin to mold. However, due to its inorganic nature, plastic rice will remain clear of mold.
By performing these simple tests, you can gain a better understanding of the quality and authenticity of the rice you’re consuming.
Consuming plastic rice poses serious health risks, as the synthetic materials are not designed for human consumption. Ingesting these imitation grains can lead to a range of gastrointestinal problems, including nausea, vomiting, and potential long-term complications. Moreover, by ensuring the authenticity of your rice, you can be confident that you’re consuming a nutritionally beneficial grain that supports your overall well-being.
To minimize the risk of encountering plastic rice, it’s advisable to purchase your rice from reputable sources, such as trusted grocery stores or local markets. Familiar brands that adhere to food safety standards are less likely to sell adulterated products. Additionally, look for certifications and quality seals on the packaging that indicate the rice has been tested and approved for safety.
While the prevalence of plastic rice may be a subject of debate, the potential health risks associated with consuming adulterated grains cannot be ignored. By understanding the characteristics of genuine rice and performing the simple tests outlined in this guide, you can take an active role in safeguarding your family’s health and well-being. Remember, a little vigilance goes a long way in maintaining a safe and nutritious diet.