Dementia is a growing global concern, affecting millions of people and their families. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for timely interventions that can help manage symptoms, slow progression, and enhance quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the early signs of dementia, how to recognize cognitive and behavioral changes, and lifestyle adjustments you can make to combat its effects.
Understanding Dementia and the Importance of Early Detection
Dementia isn’t a single disease but a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities. Conditions like Alzheimer’s, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia fall under this umbrella. Detecting it early allows for more effective management, helping those affected maintain independence longer. For families, early detection provides a window to prepare, access support, and make informed decisions about future care.
Common Early Signs of Dementia
Early symptoms of dementia can be subtle and often go unnoticed. Familiarizing yourself with these signs can help identify the condition early:
- Memory Loss: Forgetting recently learned information is one of the most noticeable signs. People may frequently ask the same questions or rely heavily on reminders.
- Difficulty with Everyday Tasks: Familiar tasks like cooking, driving to a known location, or following a recipe can become challenging.
- Language Problems: Struggling to find the right words, repeating phrases, or having trouble following conversations can indicate dementia.
- Disorientation: Losing track of time, dates, or familiar places is another common symptom.
- Decreased Judgment: This might show up as poor financial decisions or neglecting personal grooming and hygiene.
Recognizing these signs early is crucial as it leads to timely medical evaluation and management.
How to Recognize Cognitive and Behavioral Changes
Cognitive and behavioral changes are hallmarks of dementia. Here’s how to spot them:
1. Cognitive Changes
- Memory and Recall: Individuals may struggle to remember appointments or recent events.
- Problem Solving: Tasks that require planning, organizing, or performing simple calculations can become difficult.
- Following Conversations: They might frequently lose track during discussions or find it hard to follow directions.
2. Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms
- Mood Swings: Irritability, anxiety, or depression are common, especially as the individual becomes aware of their cognitive changes.
- Wandering and Agitation: Affected individuals may wander or show signs of restlessness.
- Hallucinations or Delusions: In some types of dementia, such as Lewy body dementia, hallucinations or delusions may occur.
Identifying these symptoms early can lead to a faster diagnosis and better planning.
Medical Evaluations for Diagnosing Dementia
Once early signs of dementia are observed, a thorough medical evaluation is essential. Here’s what it typically involves:
- Cognitive Tests: Tests like the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) or Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) measure memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
- Physical and Neurological Exams: Doctors assess coordination, reflexes, and eye movements, which can provide insights into the neurological aspects of dementia.
- Imaging and Lab Tests: Brain imaging, such as MRI or CT scans, can help identify changes in the brain. Blood tests can rule out other causes like vitamin deficiencies or thyroid issues.
These assessments provide a comprehensive view of a person’s cognitive health, guiding the diagnosis and treatment plan.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Combat Dementia
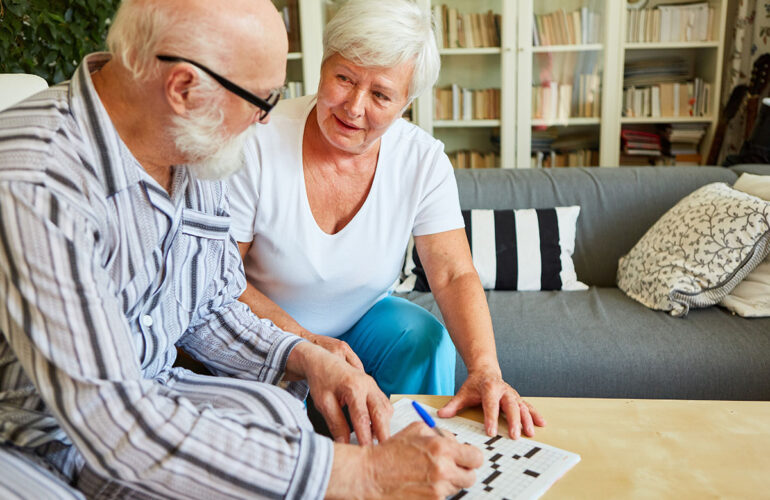

Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in reducing the risk of dementia or delaying its onset. Let’s look at some strategies:
1. Nutritional Strategies
- Mediterranean Diet: This diet emphasizes whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil and nuts, all linked to improved cognitive function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3s, such as fish and flaxseed, are beneficial for brain health.
- Antioxidants: Consuming antioxidant-rich foods can protect brain cells from damage. Berries, leafy greens, and nuts are excellent choices.
2. Physical Activity
- Regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain, which can boost cognitive function. Aim for activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. A target of at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week is recommended.
- Strength and Balance Exercises: Activities such as yoga or strength training improve balance and coordination, supporting overall health.
3. Mental Stimulation
- Cognitive Exercises: Engage in brain-stimulating activities like puzzles, reading, or learning a new skill. These activities keep the brain engaged and can strengthen neural connections.
- Social Interaction: Staying socially active reduces stress and provides emotional support. Regularly interacting with friends or participating in group activities can have protective effects against cognitive decline.
4. Managing Stress and Emotional Well-being

- Chronic stress can contribute to cognitive decline. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Emotional Health: A strong support network and healthy coping strategies are essential for maintaining emotional well-being. Mental health support, like counseling, can also be beneficial.
Medical Treatments and Support for Dementia Patients
While there is no cure for dementia, certain medications can help manage symptoms:
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Drugs like donepezil and rivastigmine improve memory and attention in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Memantine: This medication helps manage moderate to severe symptoms by improving cognitive functions.
- Additional Support: Treating symptoms such as anxiety or depression with appropriate medications can also help improve quality of life. A network of support services, including in-home care, support groups, and educational resources, is invaluable for patients and caregivers alike.
Caregivers should prioritize their well-being, seeking respite care or support groups to prevent burnout and maintain their physical and emotional health.
Conclusion: Proactive Steps to Detect and Combat Dementia
Detecting dementia early and taking proactive steps can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected. By recognizing the symptoms, undergoing relevant evaluations, and making lifestyle changes, individuals can protect their cognitive health. Proper nutrition, regular physical activity, mental stimulation, and social engagement are powerful tools in combating dementia. Although the journey can be challenging, a comprehensive approach combining medical treatments and strong support networks can make a meaningful difference. With the right knowledge and actions, it’s possible to manage dementia effectively and improve overall well-being.


