Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that supports numerous bodily functions, from maintaining bone health to boosting the immune system. Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” it helps our bodies absorb calcium, regulate phosphorus levels, and maintain a healthy immune response. However, many people don’t get enough vitamin D, and deficiency can lead to serious health complications.
Understanding Vitamin D and Its Importance
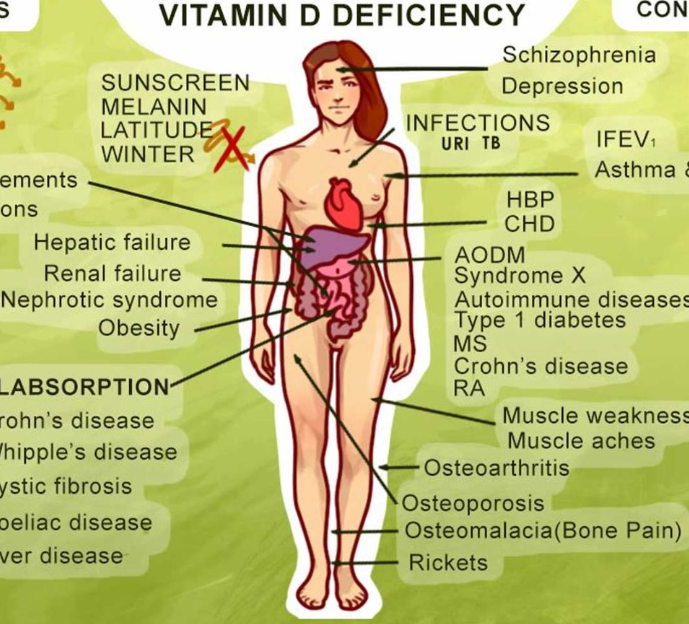
Vitamin D is vital for overall well-being. Not only does it promote strong bones and teeth, but it also supports the immune system, brain, and nervous system. In addition, it helps regulate insulin levels and supports lung function and cardiovascular health. Without adequate vitamin D, these functions can falter, leading to a wide range of health problems.
How Vitamin D Deficiency Occurs
Vitamin D deficiency can occur due to various factors. Insufficient exposure to sunlight is a common cause, especially for those living in areas with long winters or people who spend most of their time indoors. Poor dietary intake, absorption issues, and certain medical conditions can also contribute to low vitamin D levels. Those with darker skin tones may require more sunlight to produce adequate vitamin D due to higher melanin levels.
10 Vital Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
Recognizing the early signs of vitamin D deficiency is critical for preventing more serious health complications. Here are the top 10 symptoms that may indicate you’re running low on this essential nutrient.
1. Unexplained Fatigue and Tiredness
Do you feel constantly tired, even after a full night’s sleep? Vitamin D plays a significant role in energy production. Low levels can result in chronic fatigue, making you feel drained and exhausted without any clear reason. If you’re always tired despite adequate rest, it might be time to check your vitamin D levels.
2. Frequent Illnesses and Infections
One of vitamin D’s most important functions is supporting the immune system. If you find yourself catching colds or infections more frequently than usual, it could be due to low vitamin D. This deficiency weakens the immune system, leaving you more vulnerable to infections like colds, flu, and respiratory issues.
3. Bone and Back Pain
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy bones because it helps the body absorb calcium. A lack of vitamin D can lead to chronic bone pain, particularly in the back and joints. If you experience persistent pain in your bones or lower back, it could be a sign that your vitamin D levels are too low.
4. Depression and Low Mood
There’s a well-documented connection between vitamin D deficiency and mood disorders, including depression. Vitamin D receptors in the brain play a role in mood regulation, and low levels of this nutrient have been linked to an increased risk of depression, especially in the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
5. Impaired Wound Healing
Slow wound healing is another sign of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D promotes the production of compounds essential for wound healing and helps control inflammation. If your cuts and scrapes take longer than usual to heal, it could indicate that you need more vitamin D.
6. Hair Loss
While hair loss can result from various factors, severe hair loss may be linked to vitamin D deficiency. This vitamin helps regulate the hair follicle cycle, and low levels can disrupt hair growth, potentially contributing to conditions like alopecia, which leads to patchy hair loss.
7. Muscle Pain
Chronic muscle pain is another symptom of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D supports muscle function, and its deficiency can lead to persistent pain or discomfort. If you experience unexplained muscle aches, especially after periods of rest or inactivity, it could be due to low vitamin D levels.
8. Bone Loss
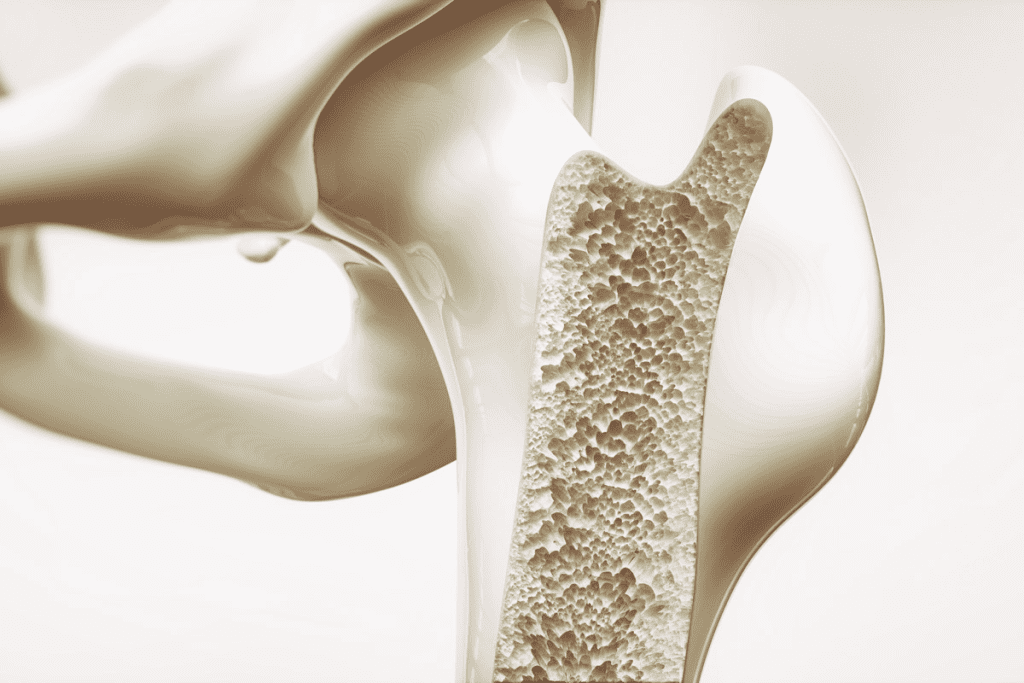

Over time, low vitamin D levels can lead to a reduction in bone density, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is necessary for strong bones. Without enough vitamin D, your bones can become weak and brittle.
9. Digestive Issues
Certain digestive disorders, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease, can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D, leading to deficiency. If you have any of these conditions and are experiencing symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, consult your doctor about managing your nutrient levels.
10. Weight Gain and Obesity
There’s emerging evidence suggesting that low vitamin D levels may contribute to weight gain and obesity. Vitamin D is involved in regulating metabolic processes, and a deficiency may impair your body’s ability to efficiently metabolize fat. If you’re struggling with unexplained weight gain, consider checking your vitamin D levels.
How to Diagnose Vitamin D Deficiency

If you suspect you have a vitamin D deficiency, the first step is to get a blood test, specifically the 25-hydroxy vitamin D test. This test measures the amount of vitamin D in your blood, allowing healthcare providers to determine if you need dietary adjustments or supplements.
Effective Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Treating and preventing vitamin D deficiency is relatively straightforward. Here’s what you can do:
- Get More Sunlight: Spending 15 to 30 minutes in direct sunlight several times a week can help your body naturally produce vitamin D. Make sure to expose your skin, as sunlight needs to hit your skin directly to trigger vitamin D production.
- Eat Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Incorporate foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, and tuna), fortified dairy products, eggs, and mushrooms into your diet. These are excellent sources of vitamin D.
- Take Vitamin D Supplements: If your blood test confirms a deficiency, your doctor may recommend vitamin D supplements. Be sure to follow their dosage advice, as too much vitamin D can cause toxicity.
- Address Absorption Issues: If you have a digestive disorder that affects nutrient absorption, work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure you’re getting enough vitamin D.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is more common than you might think, and its effects can be far-reaching—from chronic fatigue to bone loss and mood disturbances. Recognizing the signs early and taking steps to boost your vitamin D levels can improve your overall health and well-being. Whether through sunlight, diet, or supplements, ensuring you get enough vitamin D is essential for maintaining strong bones, a robust immune system, and a positive mood. Don’t ignore these warning signs—addressing a vitamin D deficiency today can help you avoid more serious health issues tomorrow.


