Foot pain is something that almost everyone experiences at some point in life. Whether it’s caused by an injury, overuse, or an underlying condition, foot pain can greatly affect your quality of life. The good news is that identifying the root cause of the pain can help you find the right treatment and get back to your daily routine pain-free. In this article, we will explore ten common reasons for foot pain and provide actionable solutions to help you alleviate discomfort and maintain healthy feet.
Understanding the Common Causes of Foot Pain
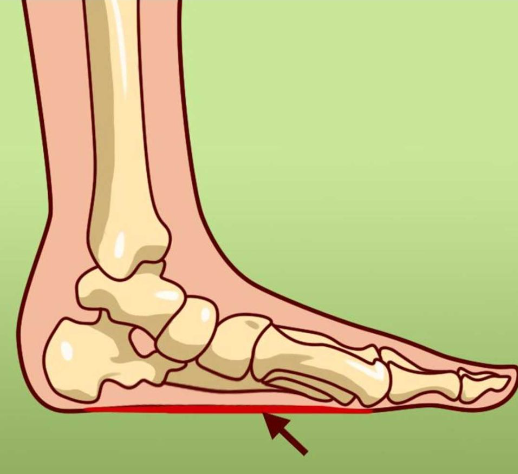
Foot pain can originate from a variety of sources, ranging from biomechanical problems like flat feet to inflammatory conditions such as gout. Identifying the cause of your foot pain is crucial because it helps guide you toward the correct treatment. Below, we’ll break down ten frequent causes of foot pain and what you can do to address each issue effectively.
Reason 1: Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of foot pain, particularly in the heel. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed. The pain is typically sharp and most intense during the first steps in the morning.
How to Fix Plantar Fasciitis:
- Rest and avoid activities that aggravate the condition.
- Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes to reduce inflammation.
- Stretch your calf muscles and the plantar fascia regularly.
- Use supportive footwear or insoles with good arch support.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help, but if the pain persists, physical therapy or corticosteroid injections might be necessary.
Reason 2: Bunions
A bunion is a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. It can cause pain, swelling, and redness and may make it uncomfortable to wear tight or narrow shoes. Bunions often develop due to genetics, improper footwear, or arthritis.
How to Fix Bunions:
- Wear shoes with a wide toe box to relieve pressure.
- Use padding or orthotics to cushion the bunion.
- Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Severe cases may require surgical intervention to realign the joint and remove the bunion.
Reason 3: Corns and Calluses
Corns and calluses form due to repetitive friction or pressure on the skin. They are hardened layers of skin that can develop on the toes or soles of the feet and cause discomfort.
How to Fix Corns and Calluses:
- Soak your feet in warm water to soften the skin.
- Gently rub a pumice stone over the area to remove thickened skin.
- Apply moisturizing lotions to prevent dryness.
- Wear well-fitting shoes to prevent recurrence, and use protective pads for added cushioning.
Reason 4: Heel Spurs
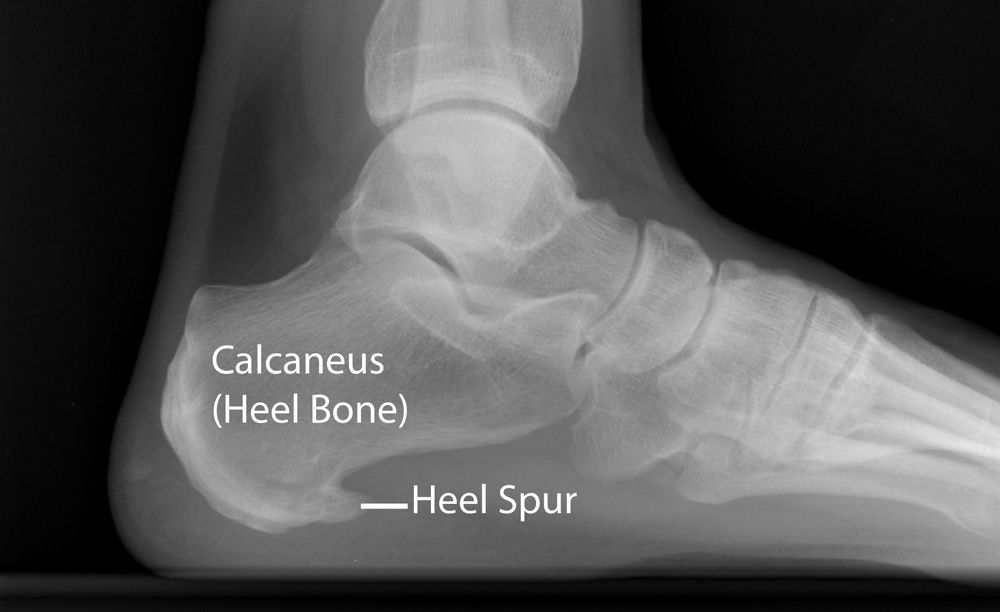
Heel spurs are bony outgrowths that develop on the underside of the heel bone, often as a result of prolonged strain on the muscles and ligaments. They are frequently associated with plantar fasciitis and can cause sharp, stabbing pain when walking or standing.
How to Fix Heel Spurs:
- Rest and apply ice to reduce inflammation.
- Stretching exercises for the calves and Achilles tendon can help alleviate tension on the heel.
- Orthotic inserts can provide added support.
- Anti-inflammatory medications can offer temporary relief, and in severe cases, surgery might be necessary.
Reason 5: Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis occurs when the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, becomes inflamed. This condition often results in pain and stiffness in the back of the heel, particularly after periods of activity or rest.
How to Fix Achilles Tendinitis:
- Rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain.
- Apply ice to the back of the heel for pain relief.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises can promote healing.
- Wear shoes with good support and cushioning.
- In severe cases, physical therapy or the use of a brace may be necessary to prevent further damage.
Reason 6: Metatarsalgia
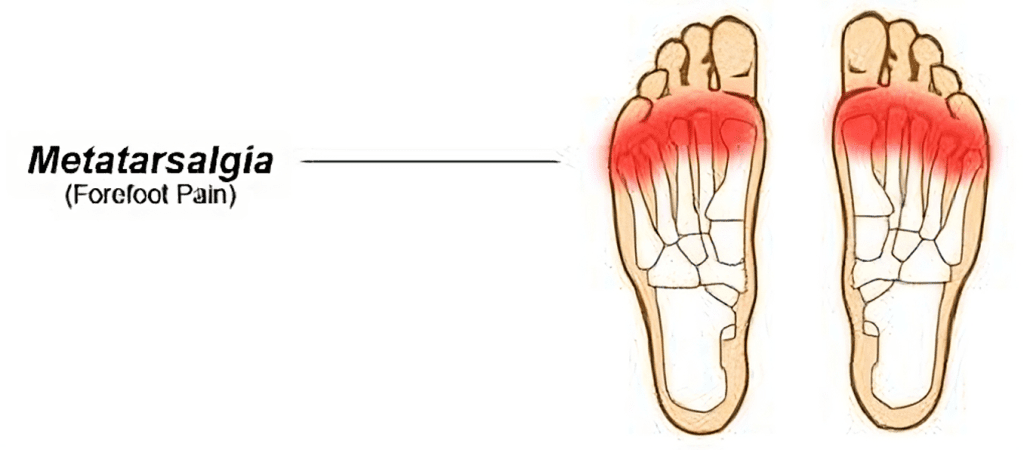
Metatarsalgia is characterized by pain in the ball of the foot, often caused by overuse, high-impact activities, or wearing shoes with inadequate support. The condition can cause sharp or aching pain in the metatarsal region, making it difficult to walk or stand for extended periods.
How to Fix Metatarsalgia:
- Rest and apply ice to the painful area.
- Switch to footwear with proper cushioning and support.
- Use insoles or orthotics to redistribute pressure on the foot.
- Engage in low-impact activities to reduce stress on the foot.
Reason 7: Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a thickening of tissue around a nerve leading to the toes, most commonly between the third and fourth toes. This condition can cause sharp, burning pain, numbness, or a sensation that you have a pebble in your shoe.
How to Fix Morton’s Neuroma:
- Wear shoes with a wider toe box to reduce pressure on the nerve.
- Use orthotic inserts to support the foot and relieve pressure.
- Anti-inflammatory medications can help manage pain.
- In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be required to remove the affected tissue.
Reason 8: Flat Feet
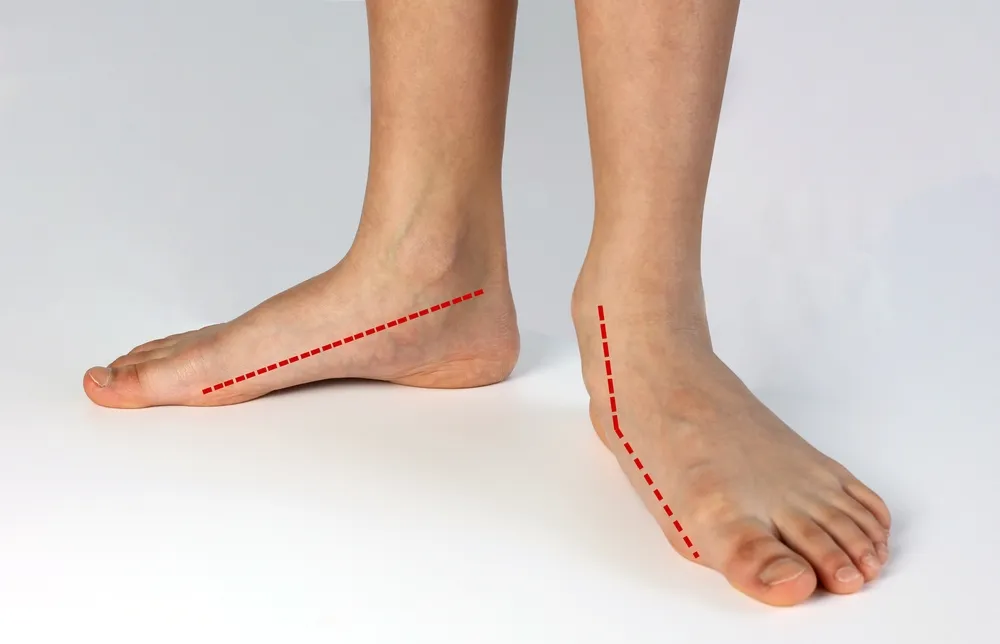
Flat feet, also known as fallen arches, occur when the arches of the feet collapse, causing the entire foot to make contact with the ground. This condition can result in pain in the arches and heels and may lead to other issues such as shin splints or knee pain.
How to Fix Flat Feet:
- Wear supportive shoes or custom orthotics to provide arch support.
- Incorporate foot-strengthening and stretching exercises into your routine.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the arches.
- Physical therapy may be recommended, and in severe cases, surgery might be necessary.
Reason 9: Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, particularly affecting the big toe. It can cause intense pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint, often triggered by certain foods or dehydration.
How to Fix Gout:
- Take medications to reduce pain and inflammation, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids.
- Adopt lifestyle changes to lower uric acid levels, including avoiding foods high in purines, such as red meat and shellfish.
- Stay hydrated to help flush excess uric acid from the body.
- Prescription medications may be required to prevent future gout attacks.
Reason 10: Stress Fractures
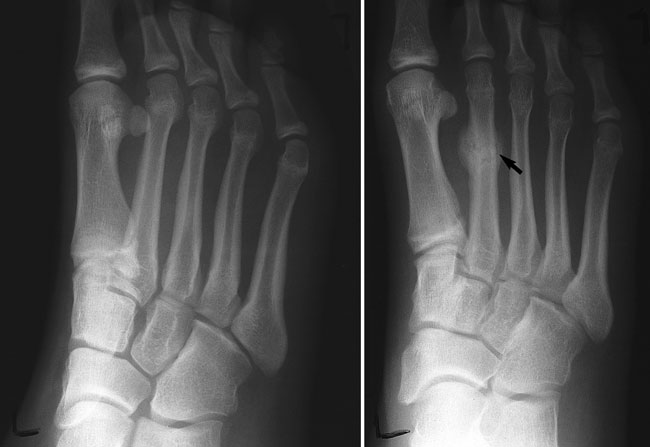
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in the bones of the foot, typically caused by repetitive force or overuse. These fractures commonly occur in the weight-bearing bones of the foot and can result in localized pain, swelling, and tenderness.
How to Fix Stress Fractures:
- Rest and avoid any weight-bearing activities until the fracture heals.
- Ice the affected area to manage pain and reduce swelling.
- Use a protective boot or brace to stabilize the foot.
- Gradually return to activity under medical supervision to avoid re-injury.
Preventive Measures for Foot Pain
Preventing foot pain is often as simple as taking proper care of your feet. Here are some tips to maintain foot health and avoid common issues:
- Wear well-fitting shoes that offer adequate support and cushioning.
- Avoid high-impact activities or repetitive motions that strain the feet.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet.
- Incorporate foot-strengthening and stretching exercises into your routine.
- Practice good foot hygiene by keeping your feet clean and moisturized.
When to Seek Medical Attention

While many causes of foot pain can be treated at home, there are times when you should seek professional help. If your foot pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by swelling, redness, or fever, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you experience numbness, tingling, or difficulty walking, don’t delay seeking medical advice.
Foot pain is more than just an inconvenience—it can disrupt your daily life and impact your overall well-being. By understanding the common causes and implementing the appropriate treatments, you can take control of your foot health. Remember to prioritize preventive measures and address any issues promptly to keep your feet strong, healthy, and pain-free. If your symptoms persist, seeking medical attention is crucial for preventing further complications and ensuring a faster recovery. Proper foot care is essential for long-term mobility and comfort, so don’t overlook the importance of addressing foot pain when it arises.


