Gluten has earned the nickname “silent killer” due to its potential to cause widespread damage in the body, often without the person even realizing it. For those who are sensitive or intolerant to gluten, its consumption can lead to a host of chronic health issues. Identifying gluten sensitivity early can help mitigate these risks and lead to better health outcomes. Let’s explore the nine signs that might indicate you’re gluten sensitive and why it’s crucial to pay attention to them.
1. Gastrointestinal Problems

One of the most common signs of gluten sensitivity is trouble with the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms like nausea, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and even constipation are frequently reported by those who are sensitive to gluten. These issues are often misattributed to other conditions, such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). In fact, studies suggest that up to 15% of the global population is diagnosed with IBS, many of whom might actually have undiagnosed gluten sensitivity. This misdiagnosis can lead to improper treatment, leaving symptoms unresolved.
2. Unexplained Weight Changes
Another indicator of gluten sensitivity is unexplained changes in weight. Whether it’s sudden weight loss or unexpected weight gain, these fluctuations can be a sign that something is off. Gluten sensitivity can trigger inflammation at the cellular level, disrupting normal metabolic processes. If you’ve noticed significant weight changes that don’t correspond to your diet or lifestyle, and they’re accompanied by other symptoms of malabsorption, gluten might be the culprit.
3. Hormonal Imbalance
Gluten sensitivity can also wreak havoc on your hormones. There’s a direct link between gluten intolerance and hormonal imbalances, which can manifest as irregular menstrual cycles, unexpected weight changes, PMS, and sleep disturbances. These hormonal issues are particularly prevalent during times of significant hormonal shifts, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Women, in particular, should be mindful of these signs, as they are more likely to experience gluten-related hormonal disruptions.
4. Central Nervous System Issues
Gluten sensitivity doesn’t just affect your gut—it can also impact your brain. When you consume gluten, it can increase inflammation and permeability in the intestines, which in turn can lead to issues with concentration, depression, anxiety, insomnia, and general fatigue. Many individuals with gluten intolerance report feeling irritable, easily distracted, and having trouble focusing. Furthermore, migraines are more common in those who are gluten sensitive, with headaches often occurring 30 to 60 minutes after eating gluten-containing foods.
5. Skin and Nail Problems
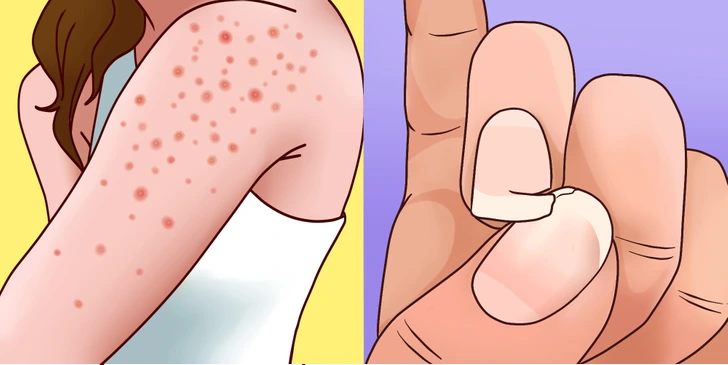
Your skin and nails can also offer clues about gluten sensitivity. Conditions like hair keratosis and herpetiform dermatitis, which cause itchy rashes on the hands, torso, face, buttocks, elbows, and hairline, are directly linked to gluten intolerance. Additionally, those who are sensitive to gluten may notice their nails becoming brittle and more prone to breaking. Other skin issues, such as eczema, can also flare up as a result of gluten-induced blockages in the body.
6. ADHD Symptoms
Gluten sensitivity may contribute to symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in both children and adults. Those with ADHD often struggle with maintaining attention and controlling impulses. A growing body of research suggests that a gluten-free diet can help alleviate some of these symptoms, leading to better focus and behavior in those with ADHD.
7. Dental Health Issues
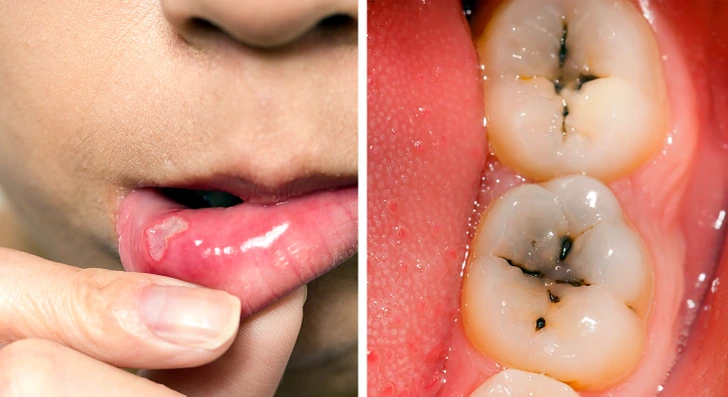
If you take good care of your teeth but still experience dental problems, gluten could be to blame. Gluten sensitivity can impair the absorption of essential nutrients and minerals in the intestines, including calcium. This can lead to issues like tooth decay, hypersensitivity of the enamel, cavities, and ulcers in the mouth. If you’re experiencing persistent dental problems despite good oral hygiene, it might be time to evaluate your diet for gluten.
8. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is often one of the first signs that lead to a diagnosis of Celiac disease, a severe form of gluten intolerance. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, and pale skin. The condition occurs because gluten intolerance can impair the absorption of iron in the intestine, leading to low levels of this essential mineral in the blood.
9. Autoimmune Diseases
Many people with autoimmune diseases have a history of gluten intolerance. Celiac disease itself is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the intestine in response to gluten. Unfortunately, this autoimmune reaction doesn’t just stop at the intestines. It can increase the risk of developing other autoimmune diseases, such as autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune liver disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
How to Treat Gluten Sensitivity

If you suspect that you might be gluten sensitive, the first step is to get tested. A blood test can check for antibodies typically present in people with Celiac disease. However, it’s important to continue eating gluten until you’ve had the test, as removing it from your diet beforehand can lead to inaccurate results.
Once diagnosed, the primary treatment is to eliminate gluten from your diet. This means avoiding foods that contain wheat, rye, bulgur, flour, semolina, and other gluten-containing grains. Always check food labels and opt for products labeled “gluten-free” to ensure you’re not inadvertently consuming gluten.
Conclusion: Listening to Your Body’s Signals
Gluten sensitivity is more common than many people realize, and its symptoms can be wide-ranging and severe. By paying attention to the signs your body is giving you—whether it’s gastrointestinal distress, unexplained weight changes, or skin issues—you can take proactive steps to address the problem. Eliminating gluten from your diet can lead to significant improvements in your health and quality of life. So, listen to your body, get tested if necessary, and consider making the switch to a gluten-free lifestyle if you’re experiencing any of these symptoms.


