Ear infections are a common but often painful condition that affects people of all ages. They occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear, causing inflammation, discomfort, and sometimes hearing problems. While they are more common in children, adults can also experience them. Left untreated, ear infections can lead to serious complications, including hearing loss.
If you’ve been feeling discomfort in your ear or experiencing unusual symptoms, it’s essential to recognize the early warning signs and take preventive measures. Let’s explore the six key symptoms of an ear infection and the best ways to reduce your risk of getting one.
What Is an Ear Infection and What Causes It?

An ear infection, also known as otitis media, happens when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear, the small space behind the eardrum. This infection causes fluid buildup, pressure, and inflammation, leading to pain, hearing loss, and discomfort.
Common causes of ear infections include:
- Respiratory infections (like the flu or colds) that spread to the ears
- Allergies that cause fluid buildup in the middle ear
- A blocked Eustachian tube (the passage that helps drain fluid from the ear)
- Exposure to secondhand smoke or environmental pollutants
- Excess moisture in the ears, creating a breeding ground for bacteria
Types of Ear Infections
There are three primary types of ear infections:
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM): The most common type, characterized by sudden pain, fever, and fluid buildup.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): Occurs when fluid remains trapped behind the eardrum after the infection clears, sometimes leading to hearing difficulties.
- Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion (COME): A long-lasting condition where fluid persists in the ear for months, potentially leading to hearing problems.
Video : 6 Signs You Have an Ear Infection And How to Prevent It!!
6 Signs You Have an Ear Infection
While some symptoms are obvious, others can be subtle or mistaken for minor issues. If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, you might have an ear infection and should consider seeking medical advice.
1. Persistent Ear Pain or Discomfort
The most common symptom of an ear infection is ear pain. It may feel:
- Sharp or stabbing
- Dull and throbbing
- Worse when lying down or chewing
For babies and young children, signs of ear pain may include:
- Constant ear tugging or rubbing
- Increased irritability or fussiness
- Difficulty sleeping or restlessness
If the pain doesn’t improve within a day or two, a doctor’s visit is necessary to prevent complications.
2. Itching in the Ear Canal
An itchy ear may not seem serious at first, but if accompanied by pain or discomfort, it could indicate an ear infection. Scratching the ear excessively can worsen the infection, leading to more irritation and possible fluid buildup.
3. Redness and Swelling in or Around the Ear

Swelling, redness inside or outside the ear, and warmth to the touch are common signs of inflammation. In some cases, the outer ear may appear swollen or sensitive to pressure.
If your ear looks inflamed, it’s a sign that your body is fighting an infection.
4. Drainage of Fluid from the Ear
A clear, yellow, or white fluid leaking from the ear could be a sign of an ear infection or ruptured eardrum. While some fluid drainage is normal, any persistent or foul-smelling discharge may indicate an infection that requires medical attention.
5. Muffled Hearing or Ringing in the Ears (Tinnitus)
Fluid buildup in the middle ear can cause temporary hearing loss or a sensation of blocked ears. Some people also experience ringing, buzzing, or a “full” feeling in the ear, known as tinnitus.
If your hearing suddenly worsens, or if tinnitus becomes persistent, consult a doctor immediately.
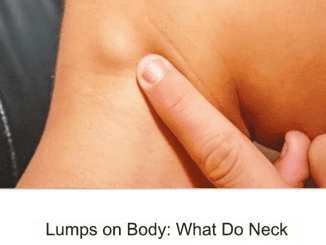
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Neck
The lymph nodes in your neck help fight off infections, so when your body is battling an ear infection, these nodes may become:
- Swollen
- Tender to the touch
- Noticeably enlarged
If you feel lumps or swelling in your neck along with ear pain, your body is likely responding to an infection.
What to Do If You Think You Have an Ear Infection

If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s best to seek medical advice to confirm whether you have an ear infection. A doctor will:
- Examine your ear using an otoscope
- Determine if the infection is viral or bacterial
- Recommend antibiotics (if necessary) or suggest pain relief methods
Ignoring an ear infection can lead to hearing loss, balance problems, or chronic infections, so early treatment is essential.
How to Prevent an Ear Infection
While ear infections can’t always be avoided, there are several ways to reduce your risk and keep your ears healthy.
Video : Ear infection in adults: symptoms, treatment and pain relief
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Washing your hands regularly can help prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses that lead to ear infections. Avoid touching your ears with unwashed hands, especially after being in crowded places.
2. Keep Your Ears Dry
Excess moisture creates a breeding ground for bacteria, increasing the risk of infections. To keep your ears dry:
- Dry them thoroughly after swimming or showering
- Avoid inserting cotton swabs or objects into your ears
- Use earplugs or a swim cap if you frequently swim
3. Avoid Exposure to Secondhand Smoke
Tobacco smoke irritates the respiratory tract and can cause fluid buildup in the middle ear, increasing the risk of infections. If possible, avoid smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.
4. Stay Up to Date on Vaccinations
Certain vaccines, like the pneumococcal vaccine and flu shot, help protect against infections that can lead to ear problems. Keeping your immunizations up to date is one of the best ways to protect yourself and your children.
5. Manage Allergies and Sinus Problems

Allergies and sinus congestion can block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup and an increased risk of infection. Managing your allergies with antihistamines or decongestants can help reduce this risk.
6. Avoid Using Cotton Swabs in the Ear
Many people mistakenly use cotton swabs to clean their ears, but this can:
- Push wax deeper into the ear canal
- Cause scratches or irritation
- Increase the risk of infections
Instead, let your ears clean themselves naturally, or use ear drops if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Ear infections can be painful and frustrating, but recognizing the early signs and taking preventive measures can help reduce your risk. If you notice ear pain, hearing loss, fluid drainage, or swelling, don’t ignore it—seek medical attention before complications arise.
By practicing good hygiene, keeping your ears dry, and addressing underlying health issues, you can significantly lower your chances of developing an ear infection. Your ears are essential for hearing, balance, and overall well-being—so take care of them!