Cancer is a heavy word that no one wants to hear, but knowing the early warning signs can be the first step to protecting your health. Anal cancer is one of those conditions that often flies under the radar, mainly because people feel uncomfortable talking about it. However, recognizing its early signs and acting quickly can be lifesaving. Here, we’ll walk you through five early warning signs of anal cancer you should never overlook—and why having these conversations can make all the difference.
1. Unexplained Rectal Bleeding

Let’s start with the most common red flag: rectal bleeding. If you notice bright red blood on your toilet paper, in your stool, or even in the toilet bowl, it’s time to pay attention. While other conditions like hemorrhoids or anal fissures might cause similar symptoms, persistent bleeding demands a closer look.
Why it happens:
Tumors or abnormal growths in the anal canal can irritate or damage nearby blood vessels, leading to bleeding.
What to do:
Don’t shrug off rectal bleeding as “just hemorrhoids.” Schedule an appointment with your doctor. They might perform a physical exam, an anoscopy, or even a biopsy to figure out what’s going on.
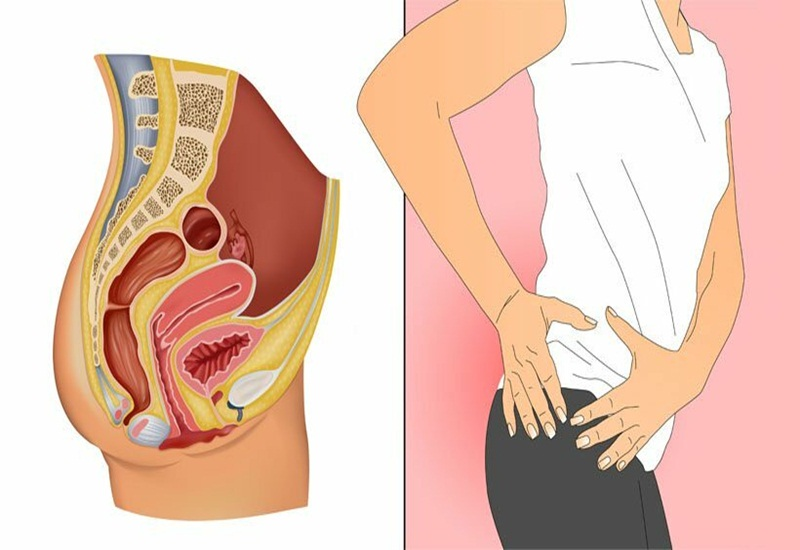
2. Persistent Pain or Discomfort
Have you been dealing with pain or an odd sense of pressure around your anal area? This isn’t something you should ignore. Painful bowel movements or constant discomfort in the anal region can be a sign of something more serious than everyday issues like constipation.
Why it happens:
As tumors grow, they press against surrounding tissues, causing inflammation, irritation, and pain.
What to do:
Don’t let the discomfort linger. Chronic or worsening pain could mean the cancer is spreading. Talk to a healthcare provider to catch it early.
3. Lumps or Growths Around the Anus
Feeling a lump or mass near your anal opening can be unsettling. These lumps might be tender or feel firm and irregular to the touch. Unfortunately, they’re often mistaken for hemorrhoids or other benign conditions.
Why it happens:
Anal cancer often begins as small, localized tumors that can grow over time. These growths may feel different from typical hemorrhoids and require further examination.
What to do:
If you find a lump, seek medical attention immediately. A doctor may recommend imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan to figure out if it’s cancerous or benign.
4. Chronic Itching or Irritation
Everyone experiences occasional itching, but if it’s persistent and paired with other symptoms like bleeding or pain, it could be a warning sign. Chronic irritation, medically known as pruritus ani, is not something to brush off.
Why it happens:
Tumors or cancerous lesions can release irritating substances, causing itchiness. Changes to the skin or tissues around the area can also contribute.
What to do:
If the itching doesn’t go away with over-the-counter remedies, it’s time to consult a doctor. Persistent irritation is your body’s way of saying something isn’t right.
5. Changes in Bowel Habits

Notice anything unusual about your bowel movements? Maybe your stool has become thinner, or you’ve been dealing with constipation or diarrhea that doesn’t seem to let up. These changes could indicate a tumor blocking or narrowing the anal canal.
Why it happens:
Tumors can obstruct the normal passage of stool, leading to noticeable changes in its shape, size, or frequency.
What to do:
Keep an eye on your bowel habits and report any persistent or unusual changes to your doctor. They may suggest a colonoscopy or other tests to determine the root cause.
Why Breaking the Silence Matters
Talking about anal cancer isn’t easy, but it’s necessary. This type of cancer often comes with a stigma, especially because of its connection to sexual health. Unfortunately, this embarrassment can delay diagnoses, making the disease harder to treat.
Certain factors, like HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection, a history of anal warts, smoking, or a weakened immune system, can increase your risk of developing anal cancer. That’s why discussing symptoms—even the uncomfortable ones—with a doctor is crucial.
Diagnosis and Treatment: What to Expect
If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, your doctor might recommend one or more diagnostic tests, such as:
- Physical examination: To check for visible lumps or abnormalities.
- Anoscopy: A closer look at the anal canal using a small, lighted scope.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample to check for cancer cells.
- Imaging tests: Scans like MRI or CT to evaluate the size and spread of the tumor.
Treatment options will depend on the stage of cancer. They often include:
- Radiation therapy: To shrink tumors and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Used alongside radiation for better results.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, surgery might be needed to remove the tumor.
How to Lower Your Risk
While not all cases are preventable, you can take steps to reduce your risk:
- Get the HPV vaccine: HPV is a major risk factor for anal cancer, and vaccination can help protect you.
- Practice safe sex: Reducing exposure to HPV and other sexually transmitted infections is essential.
- Quit smoking: Smoking weakens your immune system and increases your cancer risk.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise and a balanced diet strengthen your immune system and reduce overall cancer risk.
The Bottom Line: Early Detection Saves Lives
Anal cancer is a tough topic, but knowing the early warning signs can make all the difference. Symptoms like rectal bleeding, unusual lumps, or changes in bowel habits should never be ignored. By addressing these issues promptly, you increase your chances of early diagnosis and successful treatment.
Your health is worth more than any momentary embarrassment. So, if something feels off, don’t hesitate—act now. Spread the word, break the stigma, and prioritize your well-being. Early action can save lives, and it just might save yours.