Magnesium is one of those essential minerals that plays a critical role in keeping your body functioning smoothly. From helping produce and repair DNA to maintaining healthy bones, nerves, and muscles, magnesium is crucial to our overall well-being. Yet, despite being readily available in a variety of foods, many people—particularly teenage girls and older adults—fail to get enough through their diets. Could you be one of them? Here are 12 signs that your body may be crying out for more magnesium.
1. Low Energy Levels

Feeling constantly drained, no matter how much sleep you get? Low magnesium could be the culprit. Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, many of which are responsible for energy production. Without sufficient magnesium, your cells struggle to create and store energy efficiently, leaving you feeling fatigued.
What you can do: Try increasing your intake of magnesium-rich foods like spinach, almonds, and black beans, or consider a magnesium supplement if your diet isn’t meeting the mark.
2. Muscle Twitching or Cramping
Ever experience those annoying muscle twitches or leg cramps that seem to come out of nowhere? Magnesium plays a key role in muscle relaxation. Without it, muscles can remain tense, leading to spasms or cramps. Chronic cramping, especially during exercise, could be an indication that your magnesium levels are low.
What you can do: Incorporate more leafy greens, nuts, and seeds into your meals to help relax those muscles.
3. Frequent Headaches or Migraines
If you’re prone to headaches or migraines, low magnesium could be to blame. Magnesium regulates neurotransmitter function and blood vessel constriction, both of which are involved in migraine development. Studies show that many migraine sufferers have lower magnesium levels than the general population.
What you can do: Consuming magnesium-rich foods or taking supplements has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines in some individuals.
4. Difficulty Sleeping or Insomnia
Struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep? Magnesium has a calming effect on the nervous system, and low levels can lead to insomnia, particularly if you’re dealing with high stress. When you’re stressed, your body depletes its magnesium stores faster, making it even harder to unwind and sleep soundly.
What you can do: Consider adding magnesium-rich foods or a magnesium supplement to your nighttime routine to promote relaxation and better sleep.
5. Irregular Heartbeat
Magnesium is essential for maintaining a healthy heart rhythm. If you’re experiencing heart palpitations or an irregular heartbeat, it could be a sign that your magnesium levels are too low. Magnesium helps regulate the electrical impulses in your heart, and without enough of it, your heart can struggle to maintain a steady rhythm.
What you can do: Seek medical advice, as low magnesium levels might require more than just dietary adjustments—sometimes, supplementation or medical intervention is necessary.
6. Increased Sensitivity to Noise

Does every little sound seem to startle you or cause discomfort? This heightened sensitivity could be a result of low magnesium levels. Magnesium helps stabilize the nervous system, and without it, you may find yourself more easily irritated by loud or sudden noises.
What you can do: Boosting your magnesium intake can help calm your nerves and reduce hypersensitivity.
7. Seizures
While rare, severe magnesium deficiency can lead to seizures. Magnesium helps regulate electrical activity in the brain, and a significant deficiency can cause abnormal brain function. If you have a history of seizures, ensuring your magnesium levels are sufficient is critical.
What you can do: If seizures occur, seek immediate medical attention. Discuss magnesium levels with your doctor, as supplementation may be part of the treatment.
8. Low Bone Density
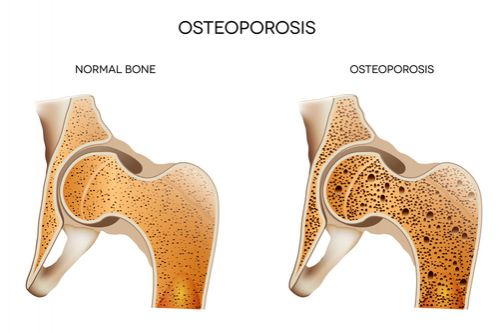
Magnesium is crucial for bone health, as about 60% of the magnesium in your body is stored in your bones. If you’re not getting enough magnesium, it can lead to lower bone density, which increases your risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
What you can do: Dairy products, fish, and green vegetables can help increase your magnesium intake, supporting stronger, healthier bones.
9. Constipation
Magnesium plays an important role in regulating bowel movements. It relaxes the muscles in the intestines, helping to move stool through the digestive tract. Low levels of magnesium can cause bowel movements to slow down, leading to constipation.
What you can do: Magnesium supplements or magnesium-rich foods like legumes and whole grains can help keep things moving smoothly.
10. High Blood Pressure

Magnesium helps relax blood vessels and regulate blood pressure. If you’re dealing with hypertension, low magnesium levels might be contributing to the problem. Studies have shown that increasing magnesium intake can help lower blood pressure, particularly in individuals with prehypertension or hypertension.
What you can do: Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can naturally support healthy blood pressure levels.
11. Type 2 Diabetes Risk
Magnesium plays a critical role in regulating insulin and glucose metabolism. Low magnesium levels are associated with a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. People with diabetes also tend to have lower magnesium levels, which can worsen insulin resistance.
What you can do: If you’re at risk for type 2 diabetes or already have it, talk to your doctor about checking your magnesium levels. A diet rich in magnesium may help manage your blood sugar.
12. Depression, Anxiety, or Mood Swings

Magnesium is sometimes referred to as the “original chill pill” because it helps regulate brain function and mood. A magnesium deficiency can lead to mood disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even confusion or irritability. Some studies have shown that magnesium supplements can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
What you can do: Consider a diet rich in magnesium or talk to your healthcare provider about supplements if you’re struggling with mood changes or emotional instability.
Conclusion: The Importance of Monitoring Your Magnesium Levels
Magnesium is vital for many of your body’s core functions, and a deficiency can lead to a wide range of symptoms. From fatigue and muscle cramps to serious conditions like seizures and heart irregularities, magnesium deficiency should not be overlooked. The good news? Magnesium is easy to find in many everyday foods, and making simple dietary changes can go a long way toward improving your health.
If you suspect you’re low on magnesium, it’s always a good idea to consult your healthcare provider. They can check your magnesium levels and recommend appropriate dietary changes or supplements. By taking control of your magnesium intake, you can boost your energy, improve your sleep, and protect your overall well-being.


